Health assessment
Since a patient is scheduled for an operation that will change their life, they are examined to exclude possible health risks. Patient’s anamnesis is collected, including self-assessment of health, history of diseases, used medications, allergies, eating habits, lifestyle, and daily physical activities.
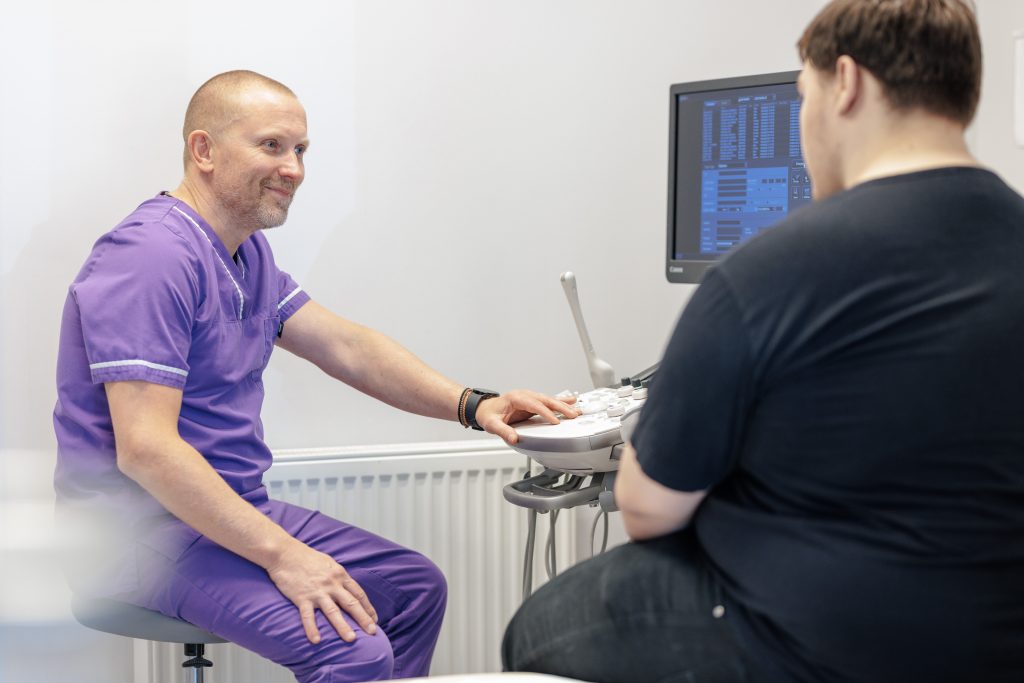
Instrumental examination
- Fibrogastroscopy (FGS)
- Electrocardiography (ECG)
- Abdominal ultrasonography (USG)
- X-ray of chest organs
In addition, echocardiography, spirometry, X-ray with oral contrast, computed tomography may be required.
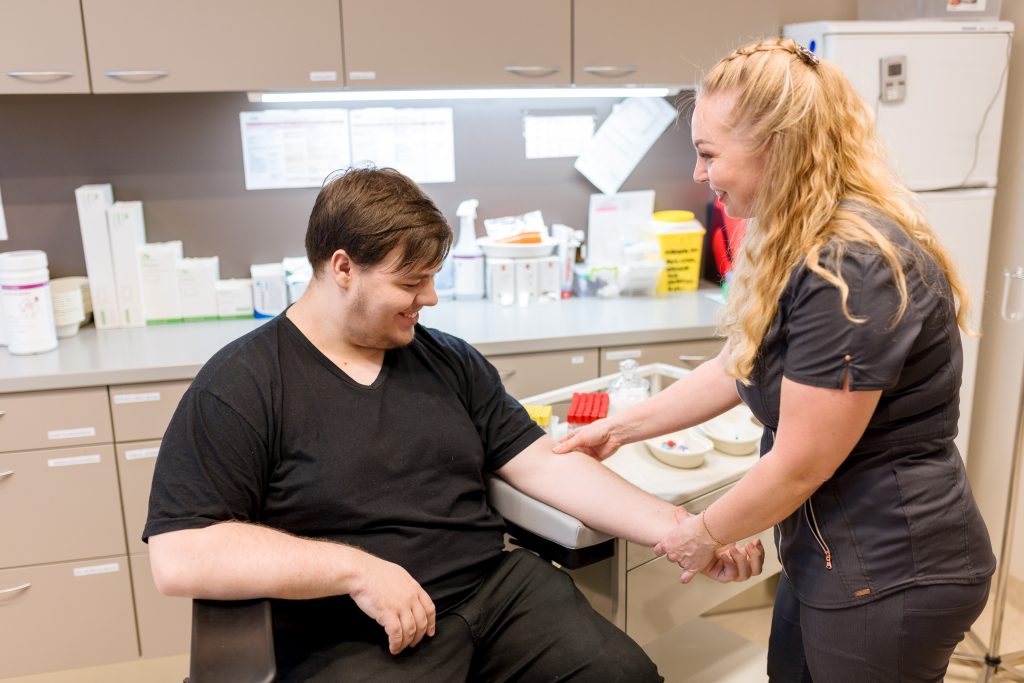
Laboratory examinations
- Full blood count
- Blood type, rhesus factor and erythrocyte antibodies
- Blood clotting indicators
- Blood biochemistry – assessment of liver, kidney, and other indicators
- Possible infections, such as hepatitis C virus, etc.
- Urine test

Specialist consultations
- Nutritionist will inform patient how eating habits will change after the operation, what products will have to be given up and what dietary habits will have to be followed in future.
- Psychologist will tell how life will change after the operation, what eating disorders will have to be dealt with, how to better organize the rhythm of life, how to adjust the lifestyle.
- Considering previous examinations, anaesthesiologist will assess anaesthesia risks, and will additionally recommend specialists, for example, in case of heart disease, the patient will most likely have to visit a cardiologist.
Consultation of pulmonologist, endocrinologist, psychiatrist may also be necessary.
Before operation, the surgeon reviews results of the examinations and specialists’ assessments and once again discusses with the patient the type of operation and possible risks.
